Definition, Formation of The Present Perfect Tense with examples, formula and sentences in English Grammar | Structure of The Present Perfect Tense.
Definition of the Present Perfect Tense:
The present perfect tense is used to talk about events or activities that happened sometime in the past or that started in the past and are still going on. It describes the relationship between past actions and present events.
What is Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense is an important part of English grammar that connects the past with the present. It is used to talk about actions or events that have happened in the past or started in the past and are still going on. Understanding this tense formation is essential for effective English communication.
For Example:
- Indefinite Past Actions: She has visited Paris. In this tense, the exact time is not specified.
- Actions Repeated in the Past: They have seen that movie several times. This tense can also indicate actions that have already happened several times before.
Formation Of The Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is formed using the 3rd form of the verb with helping verb (has, have) for affirmative or assertive sentences, interrogative sentences and negative sentences.
1. Assertive Sentence Structure of Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Tense Assertive Sentences are used to make statements about actions that ended permanently in the past or related events in the present. These statements can express facts, experiences or events that connect the past to the present.

The present perfect tense structure of assertive sentence is given.
Assertive Sentence Formula of Present Perfect Tense:
The present perfect tense formula of assertive sentence is the following;
Subject + (Helping Verb) has/have + 3rd form of verb + (Object)
Note Points:
There are some important points to form an assertive sentence in the present perfect;
- Helping verbs (Has, Have) are used after subject.
- “Has” helping verb Is used for singular noun and third-person singular pronoun (He, She, It).
- “Have” helping verb is used with plural subjects and pronoun (I, We, You, They).
- “3rd form of verb” is used after the helping verb, As (“go” becomes “gone”).
- A full stop (.) is taken at the end of the sentence to show positive sentence in the present perfect.
Assertive Sentences Examples of Present Perfect Tense:
There are some present perfect tense examples of assertive sentences;
- He has gone to school.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- She has gone to school.
(Subject: She, Helping Verb: has, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- They have gone to school.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: have, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- We have gone to school.
(Subject: We, Helping Verb: have, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- You have gone to school.
(Subject: You, Helping Verb: have, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- I have gone to school.
(Subject: I, Helping Verb: have, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- Aslam has eaten apples.
(Subject: Aslam, Helping Verb: has, 3rd form of verb: eaten, Object: apples)
- Hina has plucked the flowers.
(Subject: Hina, Helping Verb: has, 3rd form of verb: plucked, Object: the flowers)
- He has watered the plants.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, 3rd form of verb: watered, Object: the plants)
- The rain has stopped.
(Subject: The rain, Helping Verb: has, 3rd form of verb: stopped)
These sentences describe actions that continue to affect the present and indicate the connection between the past and the present.
2. Interrogative Sentence Structure of Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Tense Interrogative Sentences are used to ask questions about actions or events that happened in an uncertain situation in the past or are related to the present. These questions usually seek information about whether something has happened up to the current moment or whether an action has been completed.
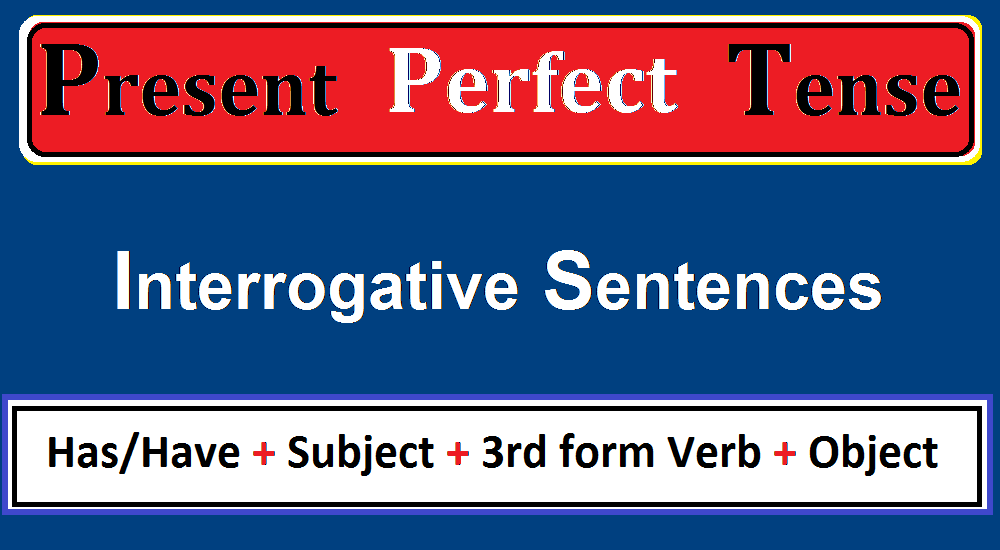
The present perfect tense structure of Interrogative sentence is given.
Interrogative Sentence Formula of Present Perfect Tense:
The present perfect tense formula of interrogative sentence is the following;
(Helping Verb) has/have + Subject + 3rd form of verb + (Object)
Note Points:
There are some important points to form an interrogative sentence in the present perfect;
- Helping verbs (Has, Have) are used before subject.
- “3rd form of verb” is used after the subject.
- A question mark (?) is taken at the end of the sentence to show the interrogative sentence.
- If interrogative words (what, where, which.etc) come in sentences, they are used at the beginning of the sentences before helping verb (has, have).
Interrogative Sentences Examples of Present Perfect Tense:
There are some present perfect tense examples of interrogative sentences;
- Has he gone to school?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: he, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- Has she gone to school?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: she, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- Have they gone to school?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: they, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- Have we gone to school?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: we, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- Have you gone to school?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: you, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- Have I gone to school?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: I, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- Has Aslam eaten apples?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: Aslam, 3rd form of verb: eaten, Object: apples)
- Has Hina plucked the flowers?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: Hina, 3rd form of verb: plucked, Object: the flowers)
- Has he watered the plants?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: he, 3rd form of verb: watered, Object: the plants)
- Has the rain stopped?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: the rain, 3rd form of verb: stopped)
- Where have you gone?
(Interrogative: Where, Helping Verb: have, Subject: you, 3rd form of verb: gone)
- When have they come to Lahore?
(Interrogative: When, Helping Verb: have, Subject: they, 3rd form of verb: come, Object: to Lahore)
- What have you done today?
(Interrogative: What, Helping Verb: have, Subject: you, 3rd form of verb: done, Object: today)
These sentences describe an indefinite period of time in past actions to ask questions that have present relevance.
3. Negative Sentence Structure of Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Tense Negative Sentences are used to indicate that nothing has happened or that something has not been completed up to the present moment. This form helps to express situations where no expected action took place.
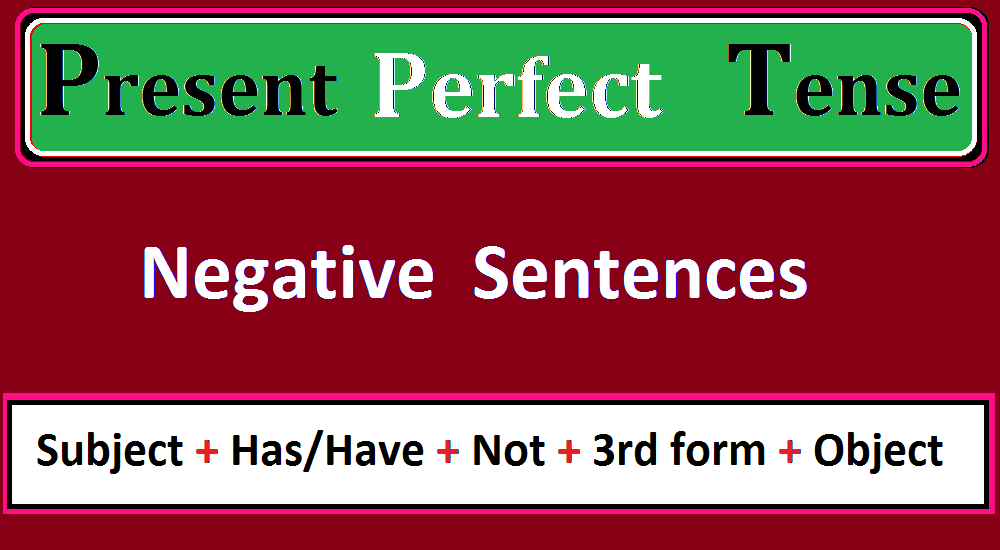
The present perfect tense structure of negative sentence is given.
Negative Sentence Formula of Present Perfect Tense:
The present perfect tense formula of negative sentence is the following;
Subject + (Helping Verb) has/have + Not + 3rd form of verb + (Object)
Note Points:
There are some important points to form a negative sentence in the present perfect;
- Helping verbs (Has, Have) are used after subject like positive sentences.
- “Not” the word is added after the helping verb (has, have ) to indicate the negative sentence.
- “3rd form of verb” is used after the word “not” .
- A full stop (.) is taken at the end of the sentence like affirmative sentence in present perfect tense.
Negative Sentences Examples of Present Perfect Tense:
There are some present perfect tense examples of negative sentences;
- He has not gone to school.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- She has not gone to school.
(Subject: She, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- They have not gone to school.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- We have not gone to school.
(Subject: We, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- You have not gone to school.
(Subject: You, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- I have not gone to school.
(Subject: I, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: gone, Object: to school)
- Aslam has not eaten apples.
(Subject: Aslam, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: eaten, Object: apples)
- Hina has not plucked the flowers.
(Subject: Hina, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: plucked, Object: the flowers)
- He has not watered the plants.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: watered, Object: the plants)
- The rain has not stopped.
(Subject: The rain, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, 3rd form of verb: stopped)
These sentences describe actions that have not been done at the present time.
Conclusion
Understanding the formation of the present perfect tense is the key to clear and accurate communication in English grammar. By understanding its structure and use, you can successfully express past and present tense experiences, ongoing actions, or recent events.

