Formation of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense with examples and sentences in English Grammar | Structure of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
Definition of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is a verb tense in which something happened in the past and continues in the present time. It is also called present perfect progressive tense.
What is Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that started in the past and are still going on over a period of time or point of time.
“Since” is used in this tense to show the point of time, as (since morning, since evening, since night, since 1970).
“For” is used in this tense to show the period of time, as (for two hours, for five days, for two nights).
Examples:
- He has been reading this book for two hours.
- We have been playing since morning.
In these examples, the sentences confirm that the actions continue for a period of time (for two hours) and a point of time (since morning).
Formation of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is formed using the first form of the verb with ing and the helping verbs (has/have) with been. Additionally, “since” and “for” are added in this tense to show time in affirmative sentences, interrogative sentences, and negative sentences.
1. Assertive Sentence Structure of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Assertive sentences are used to describe actions that started in the past and are still continuing. These sentences focus on the duration of an action.

The present perfect continuous tense structure of an assertive sentence is given.
Assertive Sentence Formula of Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
The present perfect continuous tense formula of an assertive sentence is the following:
Subject + (Helping Verb) has /have + been + 1st form of verb + ing + (object) + since/for
Note Points:
There are some important points to form an assertive sentence in the present perfect continuous;
- Helping verbs (has, have) are used after the subject.
- “Has” helping verb Is used for singular noun subject and third-person singular pronoun (He, She, It).
- “Have” helping verb is used with plural subjects and pronouns (I, We, You, They).
- “1st form of verb” is used after the helping verb.
- “Ing” is added with the 1st form of the verb, as (“go” becomes “going”).
- A full stop (.) is taken at the end of the sentence to show the positive sentence in the present perfect continuous.
Assertive Sentences Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
There are some present perfect continuous tense examples of assertive sentences;
- He has been going to school since morning.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Point of time: since morning)
- She has been going to college since morning.
(Subject: She, Helping Verb: has, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to college, Point of time: since morning)
- They have been going to school since morning.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: have, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Point of time: since morning)
- We have been going to school for an hour.
(Subject: We, Helping Verb: have, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Period of time: for an hour)
- You have been doing duty since night.
(Subject: You, Helping Verb: have, Add: been, Main Verb: do, Add: ing, Object: duty, Point of Time: since night)
- I have been going to Lahore since evening.
(Subject: I, Helping Verb: have, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to Lahore, Point of time: since evening)
- Akram has been eating apples for an hour.
(Subject: Akram, Helping Verb: has, Add: been, Main Verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: apples, Period of time: for an hour)
- Sidra has been plucking the flowers since morning.
(Subject: Sidra, Helping Verb: has, Add: been, Main verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers, Point of time: since morning)
- He has been watering the plants for an hour.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, Add: been, Main verb: water, Add: ing, Object: the plants, Period of time: for an hour)
- It has been raining since morning.
(Subject: It, Helping Verb: has, Add: been, Main Verb: rain, Add: ing, Point of time: since morning)
- Ali has been reading this book for an hour.
(Subject: Ali, Helping Verb: has, Add: been, Main verb: read, Add: ing, Object: this book, Period of time: for an hour)
- The baby has been crying since morning.
(Subject: The baby, Helping Verb: has; Add: been; Main Verb: cry; Add: ing; Point of time: since morning)
- They have been weeping since evening.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: have, Add: been, Main Verb: weep, Add: ing, Point of time: since evening)
- He has been living in this house since 1980.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, Add: been, Main verb: live; Add: ing; Object: in this house; Point of time: since 1980)
2. Interrogative Sentence Structure of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Interrogative sentences are used to ask questions about actions that started in the past and are still continuing over the duration of the action.
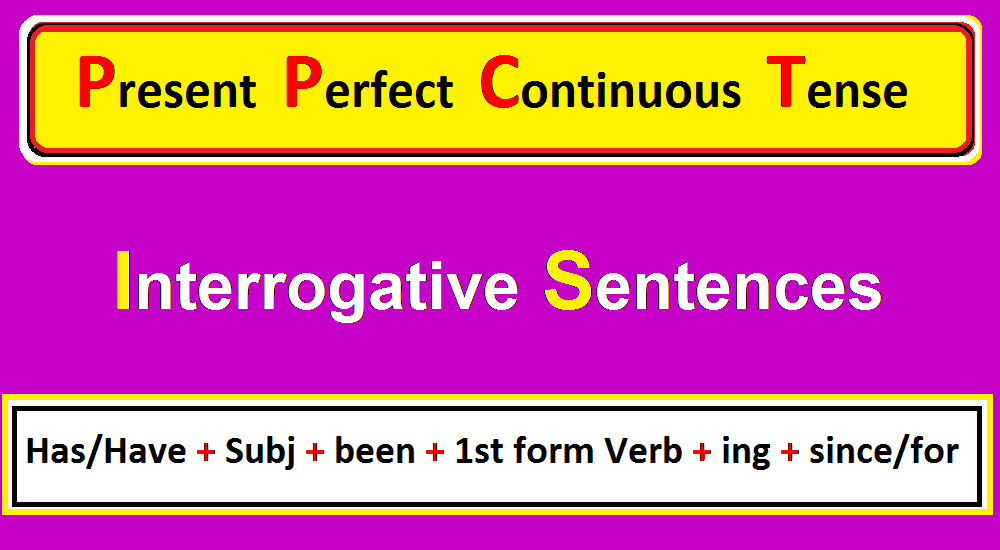
The present perfect continuous tense structure of the interrogative sentence is given.
Interrogative Sentence Formula of Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
The present perfect continuous tense formula of an assertive sentence is the following;
(Helping Verb) Has/Have + Subject + been + 1st form of verb + ing + (object) + since/for
Note Points:
There are some important points to form an interrogative sentence in the present perfect continuous;
- Helping verbs (has/have) are used before the subject.
- “1st form of verb with -ing” is used after the subject with been.
- A question mark (?) is taken at the end of the sentence to show the interrogative sentence in present perfect continuous.
- If interrogative words (what, where, which, etc.) come in sentences, they are used at the beginning of the sentences before the helping verb (has, have).
Interrogative Sentences Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
There are some present perfect continuous tense examples of interrogative sentences;
- Has he been going to school since morning?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: he, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Point of time: since morning)
- Has she been going to college since morning?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: she, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to college, Point of time: since morning)
- Have they been going to school since morning?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: they, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Point of time: since morning)
- Have we been going to school for an hour?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: we, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Period of time: for an hour)
- Have you been doing duty since night?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: you, Add: been, Main verb: do, Add: ing, Object: duty, Point of time: since night)
- Have I been going to Lahore since evening?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: I, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to Lahore, Point of time: since evening)
- Has Akram been eating apples for an hour?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: Akram, Add: been, Main verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: apples, Period of time: for an hour)
- Has Sidra been plucking the flowers since morning?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: Sidra, Add: been, Main verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers, Point of time: since morning)
- Has he been watering the plants for two hours?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: he, Add: been, Main verb: water, Add: ing, Object: the plants, Period of time: for two hours)
- Has it been raining since morning?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: it, Add: been, Main verb: rain, Add: ing, Point of time: since morning)
- Has Ali been reading this book for three hours?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: Ali, Add: been, Main verb: read, Add: ing, Object: this book, Period of time: for three hours)
- Has the child been crying since morning?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: the child, Add: been, Main verb: cry, Add: ing, Point of time: since morning)
- Have they been weeping since evening?
(Helping Verb: Have, Subject: They, Add: been, Main verb: weep, Add: ing, Point of time: since evening)
- Has he been living in this house since 1980?
(Helping Verb: Has, Subject: he, Add: been, Main verb: live; Add: ing; Object: in this house; Point of time: since 1980)
- Why has the baby been weeping since night?
(Interrogative: Why, Helping Verb: Has, Subject: the baby, Add: been, Main verb: weep; Add: ing; Point of time: since night)
These questions ask whether an action has been ongoing for a specific period of time or from a specific point in time.
3. Negative Sentence Structure of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Negative sentences are used to show that an action that was expected to continue from the past to the present is not happening. To form a negative sentence, “not” is simply added between “has/have” and “been”.

The present perfect continuous tense structure of a negative sentence is given.
Negative Sentence Formula of Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
The present perfect continuous tense formula of a negative sentence is the following;
Subject + (Helping Verb) has /have + not + been + 1st form of verb + ing + (Object) + since/for
Note Points:
There are some important points to form a negative sentence in the present perfect continuous;
- Helping verbs (has, have) are used after the subject, like positive sentences.
- “Not,” the word simply is added after the helping verb (has/have) to indicate the negative sentence.
- “1st form of verb” with (ing) is used after the word “been”.
- A full stop (.) is taken at the end of the sentence, like an affirmative sentence in present perfect continuous tense.
Negative Sentences Examples of Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
There are some present perfect continuous tense examples of negative sentences;
- He has not been going to school since morning.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Point of time: since morning)
- She has not been going to college since morning.
(Subject: She, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to college, Point of time: since morning)
- They have not been going to school since morning.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Point of time: since morning)
- We have not been going to school for an hour.
(Subject: We, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, Add: been, Main verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school, Period of time: for an hour)
- You have not been doing duty since night.
(Subject: You, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: do, Add: ing, Object: duty, Point of time: since night)
- I have not been going to Lahore since evening.
(Subject: I, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to Lahore, Point of Time: since evening)
- Akram has not been eating apples for an hour.
(Subject: Akram, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: apples, Period of time: for an hour)
- Sidra has not been plucking the flowers since morning.
(Subject: Sidra, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers, Point of time: since morning)
- He has not been watering the plants for an hour.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main verb: water, Add: ing, Object: the plants, Period of time: for an hour)
- It has not been raining since morning.
(Subject: It, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: rain, Add: ing, Point of time: since morning)
- Ali has not been reading this book for an hour.
(Subject: Ali, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main verb: read, Add: ing, Object: this book, Period of time: for an hour)
- The baby has not been crying since morning.
(Subject: The baby, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: cry, Add: ing, Point of time: since morning)
- They have not been weeping since evening.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: have, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: weep, Add: ing, Point of time: since evening)
- He has not been living in this house since 1980.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: has, Negative: not, Add: been, Main Verb: live, Add: ing, Object: in this house, Point of time: since 1980)
These sentences indicate that the action did not take place or continued during the expected time.
Conclusion:
Understanding the present perfect continuous tense formation is a great way to form affirmative or assertive sentences, interrogative sentences, and negative sentences, as well as express actions. The structure is simple and consistent with all of the above. This will enable you to speak clearly and accurately in English grammar.

