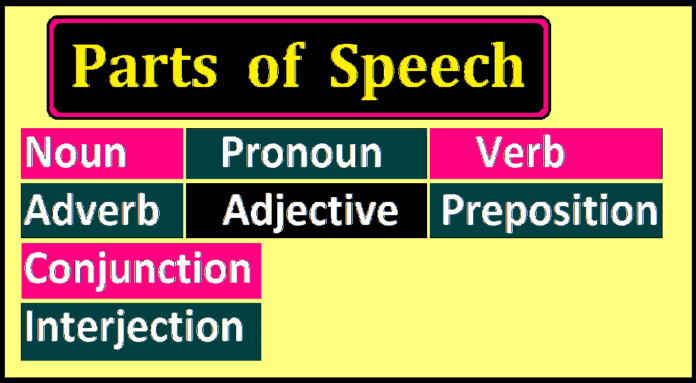
Know the eight parts of speech in English with examples: Noun, Pronoun, Adjectives, Prepositions, Verb, Adverb, Conjunctions, and Interjections. Every word in a sentence is called a part of speech that helps the meaning and organisation of the sentence.
Parts of Speech Definition:
The groups of values into which words are organised in English grammar according to their roles and functions inside sentences are known as parts of speech.
What are parts of speech in English?
Words are grouped together into parts of speech according to how they are used in sentences. There are eight primary parts of speech, and each one is important for the way in which sentences are put together and represent what they say. It enables the clear and accurate communication of information.
Different Parts of Speech with Examples
Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections are included in the eight parts of speech.
1. Nouns:
Nouns are the names we give to people, places, or things. They generally act as the foundation of the action and the subject of the sentence, which shows the reader what the sentence is about.
Simply, a noun is a naming word. It can be the name of a person , place, thing or animal.
Naming People:
Kamran, Ali, Imran, Sana and Sidra.
Naming Places:
Pakistan, Lahore, Mosque, School and London.
Naming Things:
Umbrella, Ball, Fan, Bag, Book and Pen.
Naming Animals:
Horse, Dog, Cat, Hen, Cow and Rat.

– Examples: Boy, School, Mosque, Cat, City, Book
- He goes to school.
- Allama Iqbal is our national poet.
- He is a good boy.
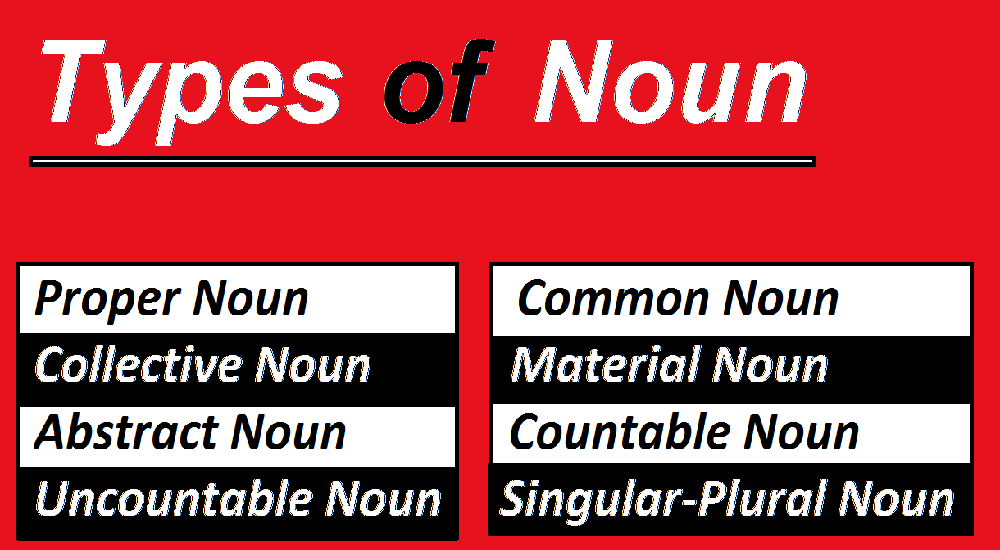
Types of Nouns
There are eight types of noun:
- Proper Noun
- Common Noun
- Collective Noun
- Material Noun
- Abstract Noun
- Singular and Plural Nouns
- Countable Noun
- Uncountable Noun
1. Proper Noun:
The names of particular people, places and things are proper nouns. They always begin with a capital letter.
(Specific names like Pakistan, Allama Iqabal, The Holy Quran, Lahore), etc.
2. Common Noun:
A common noun is a word that names common people, places or things.
(General names like City, Book, Doctor, Boy, etc.).
3. Collective Noun:
(together as a whole unit like a team, army, class, police, nation, etc.).
4. Material Noun:
(Which things are made like gold, silver, iron, wood, cotton, etc.).
5. Abstract Noun:
(Name of quality or state, like honesty, love, childhood, etc.).
6. Singular and Plural Nouns:
(Singular noun denotes one, and plural denotes more than one, like man-men, pen-pens, city-cities, etc.).
7. Countable Noun:
Nouns can also be countable (items you can count, like ‘Books or Apples’).
8. Uncountable Noun:
Uncountable (substances or concepts that you can’t count, like ‘Water or Milk’, ‘Happiness or Information’).
2. Pronouns:
Pronouns are words that place nouns in phrases to remove duplication and make them simple. They convey to people, places, things, or ideas mentioned earlier or understood from context.

– Examples: I, We, You, He, She, It, They
- He is my brother.
- How are you?
- They are coming soon.
Kinds of Pronoun
There are five types of pronoun:
1. Personal Pronouns:
(I, We, You, He), etc.
2. Reflexive Pronouns:
(Myself, Yourself, Ourselves), etc.
3. Possessive Pronouns:
(mine, yours, theirs), etc.
4. Relative Pronouns:
(who, which, that), etc.
5. Distributive Pronouns:
(Each, Either, Neither), etc.
3. Adjectives:
Adjectives are the words that modify nouns and pronouns, giving us more information about their qualities or states.
– Examples: Tall, Happy, Good, Best, Wise
- She is a good girl.
- He is my best friend.
- You are a wise student.
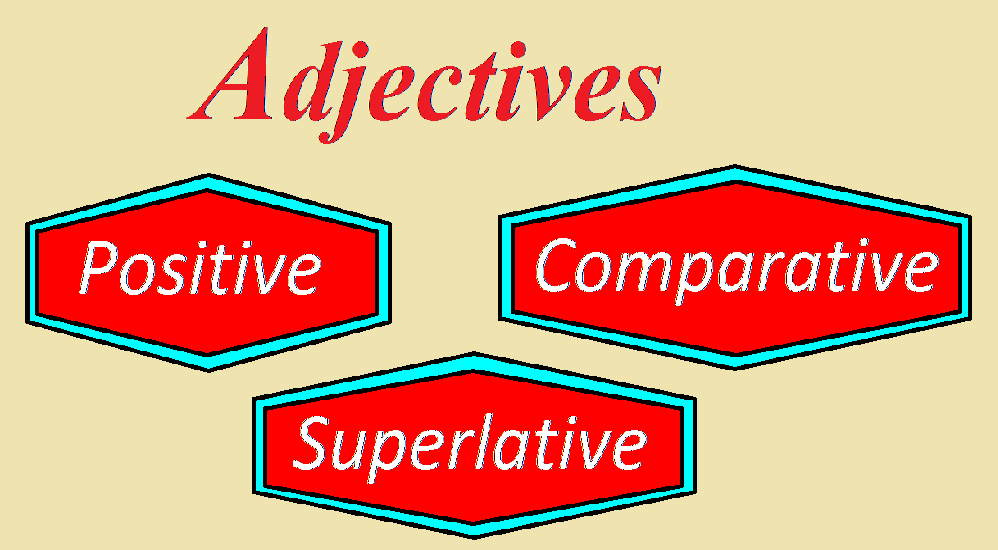
Degrees of Adjective
The degrees of comparison are three in number:
1. Positive Degree:
(Bright, Cold, Small)
2. Comparative Degree:
(Brighter, Colder, and Smaller)
3. Superlative Degree:
(Brightest, Coldest, and Smallest)
4. Verbs:
Verbs are action words that explain a subject’s actions or provide a connection for more information. They provide us with some information about a person, place, or thing.

– Examples: Tell, Run, Think, Eat, Is
- He tells a lie.
- He is a student.
- We eat rice.
Kinds of Verb
There are two main types of verb:
1. Principal Verb:
(Abide, Arise, Buy, Run), etc.
2. Auxiliary or Helping Verbs:
(Is, Am, Are, Was, Were, Has, Have, Had, Will, Shall, Do, Does, Did), etc.
5. Adverbs:
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, giving additional information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action is done.
– Examples: Always, quickly, very well, slowly
- Always speak the truth.
- He walks slowly.
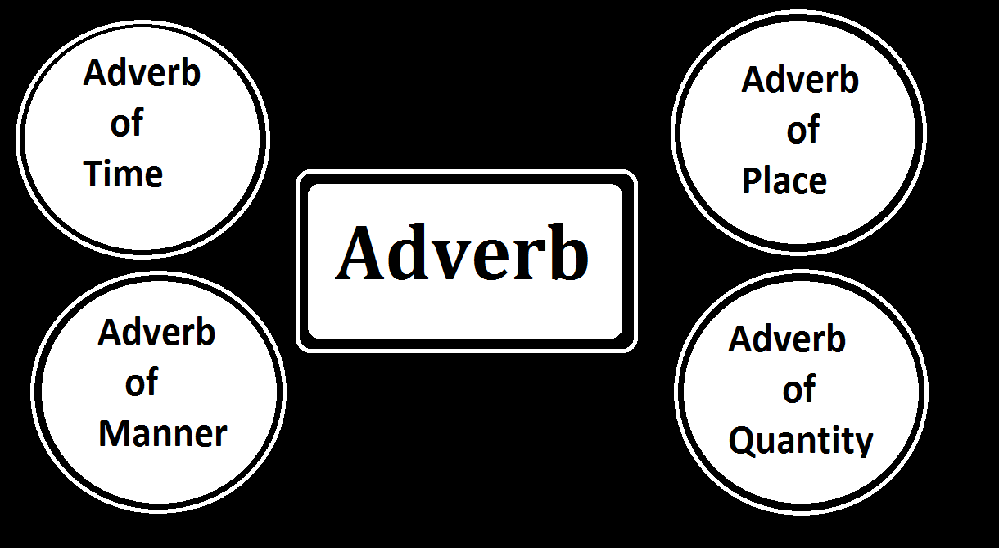
Kinds of Adverb
There are five types of
1. Adverb of Time:
(early, late, always, never, today, tomorrow, yesterday), etc.
2. Adverb of Place:
(Here, There, Near, In, Out, Up, Inside), etc.
3. Adverb of Manner:
(badly, rightly, loudly, quickly, sadly), etc.
4. Adverb of Quantity:
(Quite, Extremely, Hardly, Almost, Completely, Especially, Only, Really), etc.
5. Adverb of Number:
(Firstly, Secondly, Lastly, Once, Never, Yearly, Twice, Thrice), etc.
6. Prepositions:
Prepositions are words that indicate the direction, place, time, or manner of a noun (or pronoun) in relation to other words in a sentence.
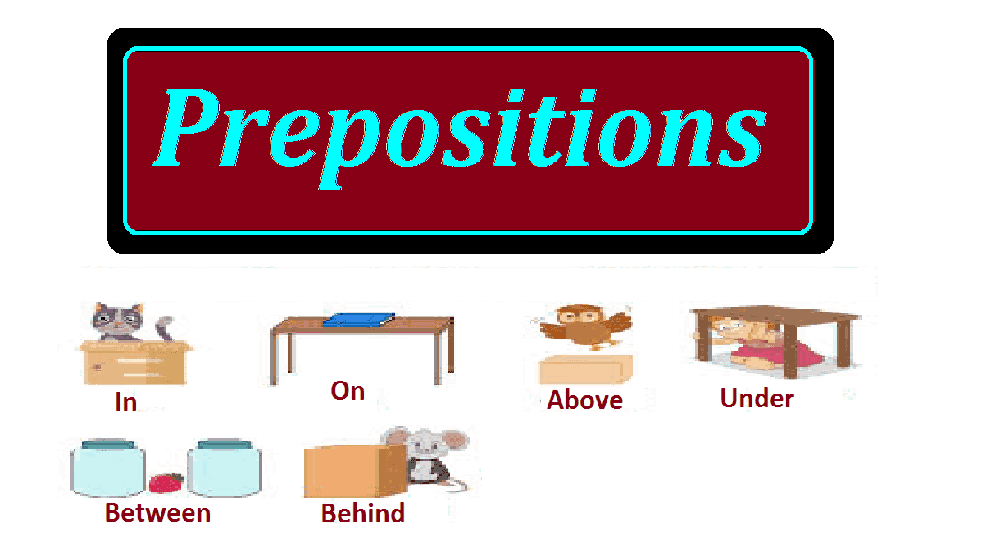
– Examples: In, On, At, By, With, From, For
- The pen is on the table.
- He agreed with me.
- Students are in the classroom.
7. Conjunctions:
Words that indicate the links between words, phrases, or clauses are known as conjunctions.
– Examples: And, But, Or, Because, Till, Until
- He is well, but I am ill.
- We work day and night.
- Ali and Akram are brothers.
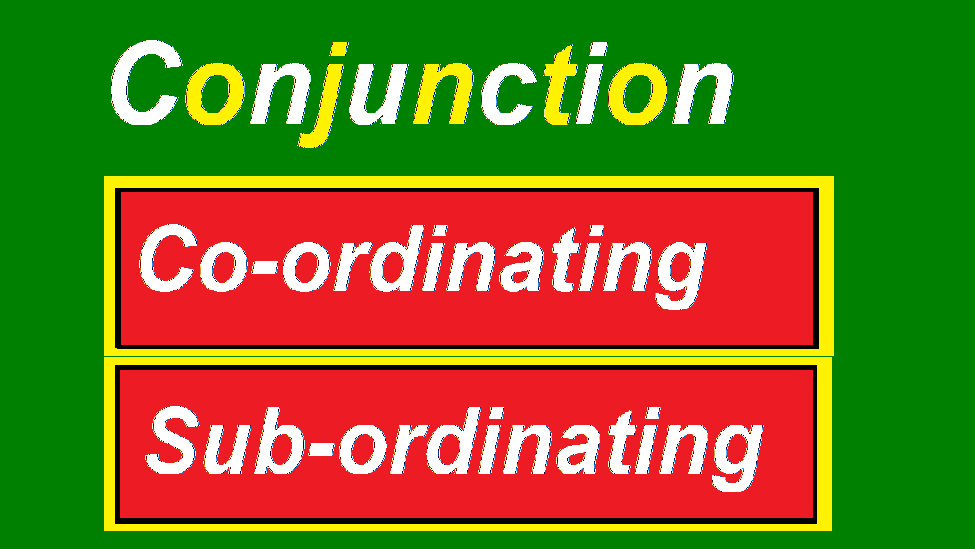
Types of Conjunctions
There are two types of conjunctions:
1. Co-ordinating conjunctions:
(And, But, Or, While, Because, If), etc.
2. Sub-ordinating conjunctions:
(Either..or, Neither..nor, Though..yet, Such..as), etc.
8. Interjections:
Interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or sudden outbreaks of feeling and usually end with an exclamation mark. They express shock, joy, sorrow, or other feelings.
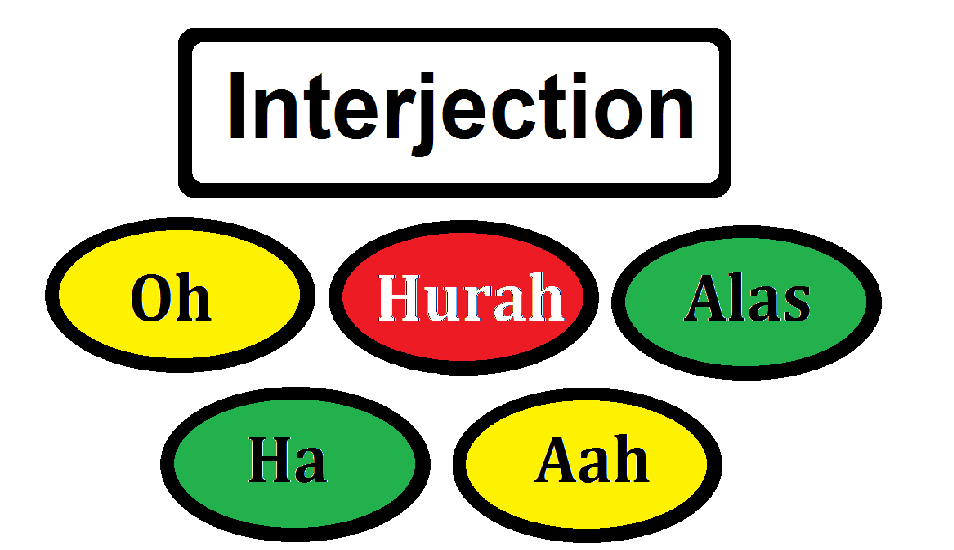
– Examples: oh!, Hurrah! Alas!, Ha!Alas!
- He is ruined.Hurrah!
- We have won the match.Oh!
- What a beautiful baby!
Conclusion:
The foundational parts of human language are the parts of speech, each of which has a specific function in constructing sentences and expressing meaning. We can communicate more effectively and clearly if we understand and use nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections correctly. Knowing these basic principles improves our capacity to communicate concepts and understand the language we use on a daily basis.