The definition Structure of the Future Perfect Tense with examples, Formation of Sentences in English Grammar, using the helping verb (will have/shall have).
How to talk about something that will be finished at a specific moment in the future? In this post, we will learn the structure of future perfect tense and how to make future perfect sentences.
Definition of the Future Perfect Tense:
The Future Perfect Tense expresses an action that will be done before a specific time in the future. Something that has not happened yet but will be completed by a certain time.
What is The Future Perfect Tense?
The future perfect tense allows us to express actions or events that will done before a certain time in the future. Whether you’re discussing future results, setting long-term goals, or planning tasks with specific dates.
It is commonly used to indicate that one event will be completed before another, or by a specific deadline.
Will have: This auxiliary verb combination indicates the future perfect tense.
Past Participle: The main verb is in the third form of the verb, as (finished, eaten, gone), etc.
For Example:
- The rain will have stopped before morning.
In this sentence, the action of stopping the rain will be completed before the morning. So, this is the future perfect sentence.
This article will provide a comprehensive presentation of future perfect tense constructions with complete examples and sentences.
The Full Structure Of Future Perfect Tense
In affirmative, interrogative, and negative sentences, the future perfect tense is formed by using the third form of the verb with an auxiliary verb (will have/shall have).
1. Assertive Sentence Structure of Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Tense Assertive sentences are used to make positive claims about actions that will take place before a certain time in the future. These sentences usually start with “will have/shall have” followed by the past participle of the main verb.

The future perfect tense structure of an affirmative sentence is given.
Positive Formula of Future Perfect Tense:
The future perfect tense formula for positive sentences is as follows.
Subject + (Helping Verb) will have/shall have + 3rd form of verb + Object
In the formation of affirmative sentences, understanding the affirmative formula of the future perfect tense will help you make the right sentences.
Note Points:
There are some important points for creating an assertive sentence in future perfect tense;
- The “third form” of the verb is used after the helping verb (will have/shall have).
- The auxiliary verbs (will have /shall have ) are used after the subject in this tense.
- “Shall have” is used with pronouns (I, We), and “Will have” is used with all singular plural nouns and pronouns.
- If two actions are finished in a sentence, the first part will be in the future perfect tense and the second part will be in the present indefinite tense.
- A full stop (.) is used at the end of a sentence to show a positive sentence in the future perfect.
Assertive Sentences Examples of Future Perfect Tense:
To form future perfect tense examples of affirmative sentence exercises are given below.
- We shall have crossed the river.
(Subject: We, Helping verb: shall have, Third form verb: crossed, Object: the river)
- They will have changed their dress.
(Subject: They, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: changed, Object: their dress)
- Sidra will have taken tea before I get up.
(Subject: Sidra, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: taken, Object: tea, Adverb: before; 2nd part: I get up)
- The rain will have stopped before they reach.
(Subject: The rain, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: stopped, Adverb: before; 2nd part: they reach)
- We shall have reached the village before the sun sets.
(Subject: We, Helping verb: shall have, Third form verb: reached, Object: the village, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the sun sets)
- The boys will have solved the questions.
(Subject: The boys, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: solved, Object: the questions)
- You will have taken breakfast.
(Subject: You, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: taken, Object: breakfast)
- I shall have acted upon the advice.
(Subject: I, Helping verb: shall have, Third form verb: acted, Object: upon the advice)
- They will have wasted their time.
(Subject: They, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: wasted, Object: their time)
- The girls will have gone to their homes.
(Subject: The girls, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: gone, Object: to their homes)
- The baby will have drunk the milk.
(Subject: The baby, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: drunk, Object: the milk)
- I shall have purchased a new house.
(Subject: I, Helping verb: shall have, Third form verb: purchased, Object: a new house)
- The patient will have died before the doctor comes.
(Subject: The patient, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: died, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the doctor comes)
- The students will have finished their work before the light goes out.
(Subject: The students, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: finished, Object: their work, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the light goes out)
- The birds will have gone to their nests.
(Subject: The birds, Helping verb: will have, Third form verb: gone, Object: to their nests)
As you can see, the positive expressions in these sentences indicate that the actions will be completed before a specific point in the future.
2. Interrogative Sentence Structure of Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Tense Interrogative sentences are used to ask questions about future perfect events. These types of questions sentences usually start with “will/shall”, followed by the subject, “have” and the third form of the verb.

The future perfect tense formation of an interrogative sentence is given.
Interrogative Formula of Future Perfect Tense:
The future perfect tense interrogative formula is as follows.
(Helping Verb) Will/Shall + Subject + have + 3rd form of verb + Object
In the formation of interrogative sentences, understanding the interrogative formula for the future perfect can help you in creating correct sentences.
Note Points:
There are some important points to form an interrogative sentence in the future perfect tense;
- In interrogative sentences, the auxiliary verb (shall/will) comes before the subject to show the interrogative sentence.
- “The third form of the verb” is used after the subject.
- A question mark (?) is placed at the end of a sentence to display the interrogative sentence in the future perfect.
- If interrogative words (what, where, who, how, etc.) happen in sentences, they are used at the beginning of the sentences before the auxiliary verb (will/shall).
Interrogative Sentences Examples of Future Perfect Tense:
Here are some examples of exercises for interrogative sentences in the future perfect tense;
- Shall we have crossed the river?
(Helping verb: Shall, Subject: we, Add: have, Third form verb: crossed, Object: the river)
- Will they have changed their dress?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: they, Add: have, Third form verb: changed, Object: their dress)
- Will Sidra have taken tea before I get up?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: Sidra, Add: have, Third form verb: taken, Object: tea, Adverb: before; 2nd part: I get up)
- Will the rain have stopped before they reach?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: the rain, Add: have, Third form verb: stopped, Adverb: before; 2nd part: they reach)
- Shall we have reached the village before the sun sets?
(Helping verb: Shall, Subject: we, Add: have, Third form verb: reached, Object: the village, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the sun sets)
- Will the boys have solved the questions?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: the boys, Add: have, Third form verb: solved, Object: the questions)
- Will you have taken breakfast?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: you, Add: have, Third form verb: taken, Object: breakfast)
- Shall I have acted upon the advice?
(Helping verb: Shall, Subject: I, Add: have, Third form verb: acted, Object: upon the advice)
- Will they have wasted their time?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: they, Add: have, Third form verb: wasted, Object: their time)
- Will the girls have gone to their homes?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: the girls, Add: have, Third form verb: gone, Object: to their homes)
- Will the baby have drunk the milk?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: the baby, Add: have, Third form verb: drunk, Object: the milk)
- Shall I have purchased a new house?
(Helping verb: Shall, Subject: I, Add: have, Third form verb: purchased, Object: a new house)
- Will the patient have died before the doctor comes?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: the patient, Add: have, Third form verb: died, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the doctor comes)
- Will the students have finished their work before the light goes out?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: the students, Add: have, Third form verb: finished, Object: their work, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the light goes out)
- Will the birds have gone to their nests?
(Helping verb: Will, Subject: the birds, Add: have, Third form verb: gone, Object: to their nests)
These sentences show the use of interrogative statements to gather information about future perfect events.
3. Negative Sentence Structure of Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Tense Negative sentences are used to indicate that an action will not end until a specific time in the future. It is emphasised that this process will remain incomplete until the upcoming deadline.
These sentences are formed by inserting “not” between “will” and “have,” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
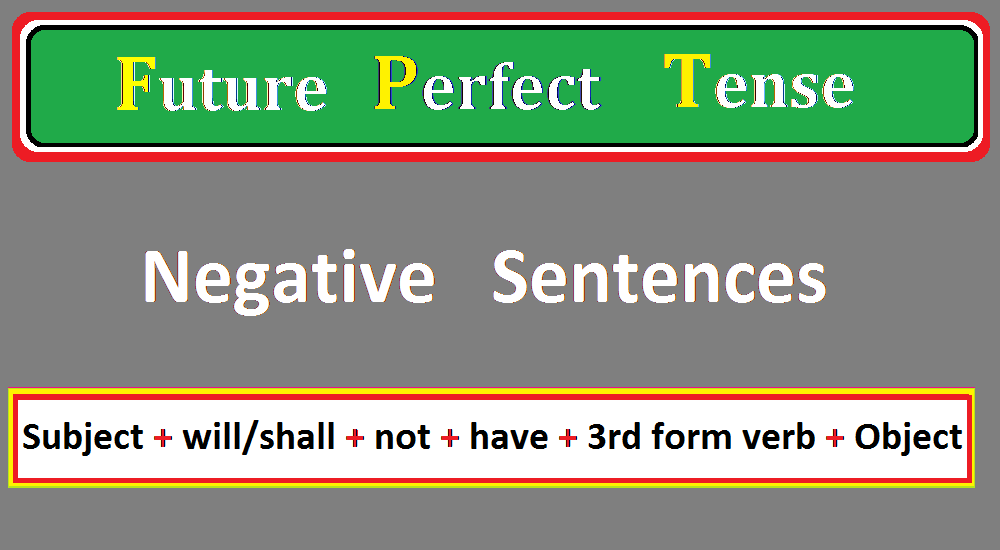
The formation of future perfect tense for a negative sentence is given.
Negative Formula of Future Perfect Tense:
future perfect tense negative formula is the following;
Subject + (Helping Verb) will/shall + not + have + 3rd form of verb + Object
Understanding the negative formula of future perfect will help you create acceptable negative sentences.
Note Points:
Here are some examples of exercises for negative sentences in the future perfect tense:
- In negative sentences, the helping verb (will /shall have) comes after the subject.
- “3rd form of the verb” is used in negative such as affirmative and interrogative sentences in the future perfect.
- The word “not” is added between the auxiliary verb (will/shall) and have to show a negative sentence.
- A full stop (.) is placed at the end of a sentence such as a positive sentence in the future perfect.
Negative Sentences Examples of Future Perfect Tense:
Here are some examples of exercises for negative sentences in the future perfect tense;
- We shall not have crossed the river.
(Subject: We, Helping verb: shall, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: crossed, Object: the river)
- They will not have changed their dress.
(Subject: They, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: changed, Object: their dress)
- Sidra will not have taken tea before I get up.
(Subject: Sidra, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: taken, Object: tea, Adverb: before; 2nd part: I get up)
- The rain will not have stopped before they reach.
(Subject: The rain, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: stopped, Adverb: before; 2nd part: they reach)
- We shall not have reached the village before the sun sets.
(Subject: We, Helping verb: shall, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: reached, Object: the village, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the sun sets)
- The boys will not have solved the questions.
(Subject: The boys, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: solved, Object: the questions)
- You will not have taken breakfast.
(Subject: You, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: taken, Object: breakfast)
- I shall not have acted upon the advice.
(Subject: I, Helping verb: shall, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: acted, Object: upon the advice)
- They will not have wasted their time.
(Subject: They, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: wasted, Object: their time)
- The girls will not have gone to their homes.
(Subject: The girls, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: gone, Object: to their homes)
- The baby will not have drunk the milk.
(Subject: The baby, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: drunk, Object: the milk)
- I shall not have purchased a new house.
(Subject: I, Helping verb: shall, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: purchased, Object: a new house)
- The patient will not have died before the doctor comes.
(Subject: The patient, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: died, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the doctor comes)
- The students will not have finished their work before the light goes out.
(Subject: The students, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: finished, Object: their work, Adverb: before; 2nd part: the light goes out)
- The birds will not have gone to their nests.
(Subject: The birds, Helping verb: will, Negative: not, Add: have, Third form verb: gone, Object: to their nests)
These sentences express that the action is not expected to be completed before a given future point.
Conclusion:
When discussing future perfect actions, it is important to understand the structure of the future perfect tense. Its structure is simple; it must be applied correctly to convey the intended meaning. In English grammar, it can be used in positive, negative, and interrogative sentences.