The Present Continuous Tense is also known as present progressive tense, learn Formation Of The Present Continuous Tense With Examples in English Grammar.
Definition of the Present Continuous Tense:
The present continuous tense, also known as the present progressive tense, is used to tell that an action or event is happening now in the present time and might go on for some time.
What is The Present Continuous Tense?
The present continuous tense is one of the most commonly used verb tenses in English grammar to represent actions happening at the time of speaking. It can also be used for upcoming programs or agreements. It suggests the constantly or temporary nature of the action for clear and accurate communication.
For Example:
- Present Action: I am reading a book.
- Constantly Action: They are studying for their exams this week.
- Future Agreement: We are meeting him tomorrow.
Formation of the Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is formed using the first form of the verb, with “ing” for positive or assertive sentences, negative sentences, and interrogative sentences.
1. Assertive Sentences
Assertive sentences in present continuous tense express actions that are happening right now or continuing. They do not express a question, a command, or an exclamation mark.
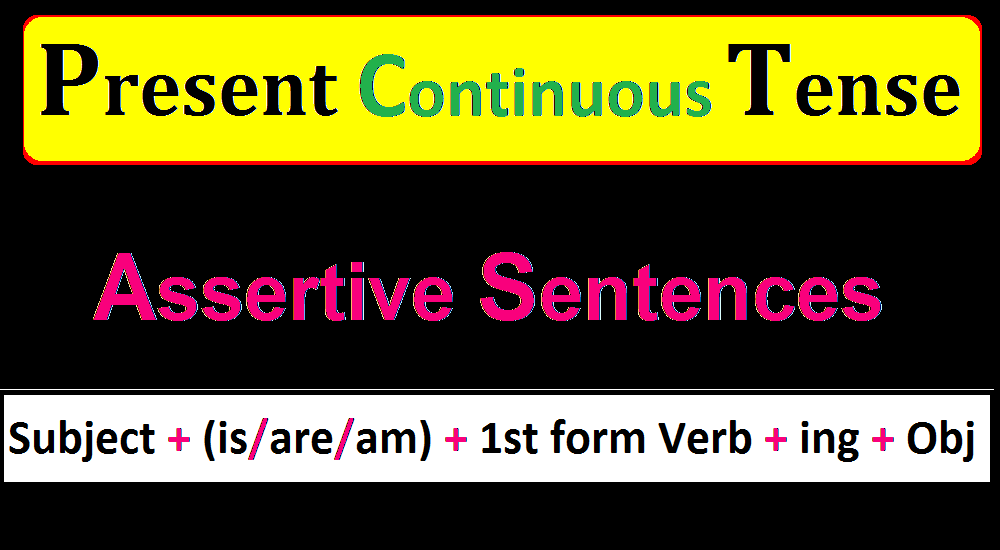
Formation of Assertive Sentence in Present Continuous Tense.
Formula of Assertive Sentence:
The formula of an assertive sentence in the present continuous tense is the following:
Subject + (Helping Verb) is/are/am + 1st form of verb + ing + (object)
Note Points:
- Helping verbs (Is, Are, Am) are used before the main verb and after the subject.
- “Is” helping verb Is used for third-person singular pronouns (He, She, It).
- “Are” helping verb is used with plural subject pronouns (We, You, They).
- “Am” helping verb is used only for pronoun the first-person singular subject (I).
- “ing” is added at the end of the base form of the verb, As (“read” becomes “reading”).
- The full stop (.) is taken at the end of the sentence to show a positive sentence in the present continuous.
Examples of Assertive Sentences:
There are some examples of assertive sentences in present continuous tenses:
- He is going to school.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: is, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- She is going to school.
(Subject: She, Helping Verb: is, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- They are going to school.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: are, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- We are going to school.(Subject: We, Helping Verb: are, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- You are going to school.
(Subject: You, Helping Verb: are, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- I am going to school.
(Subject: I, Helping Verb: am, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- It is raining.
(Subject: It, Helping Verb: is, Main Verb: rain, Add: ing)
- Aslam is eating apples.
(Subject: Aslam, Helping Verb: is, Main Verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: apples)
- They are flying kites.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: are, Main Verb: fly, Add: ing, Object: kites)
- Haroon is plucking the flowers.
(Subject: Haroon, Helping Verb: is, Main Verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers)
These sentences describe actions that are recently being performed.
2. Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences in the present continuous tense are used to ask questions about actions that are currently doing or happening.
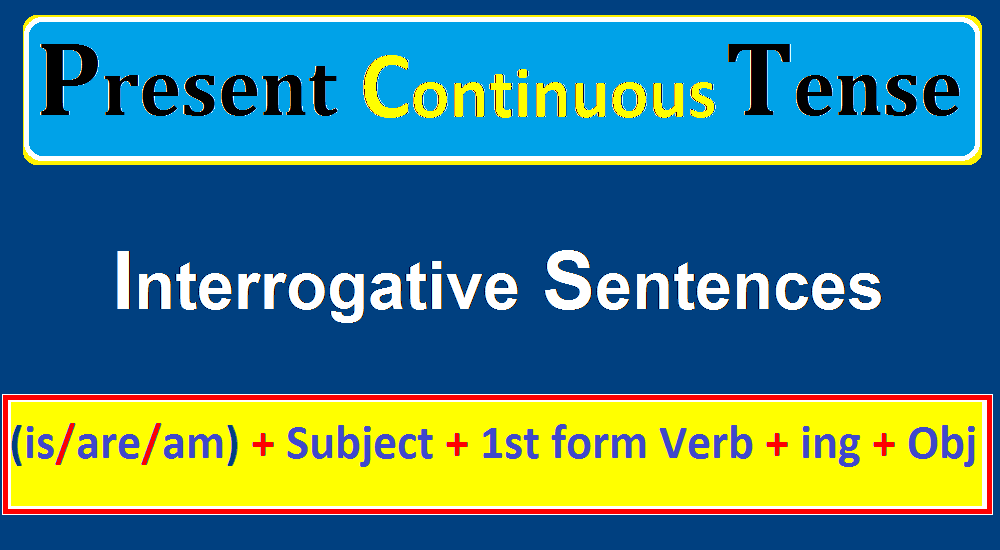
Formation of Interrogative Sentence in the Present Continuous Tense.
Formula of Interrogative Sentence:
The formula of an interrogative sentence in the present continuous tense is the following:
(Helping Verb) is/are/am + Subject + 1st form of verb + ing + (Object)
Note Points:
- The helping verb (is, are, am) comes before the subject to indicate the interrogative sentence.
- The main verb always remains the first form of the verb with “ing,” like a positive sentence in the present continuous.
- If interrogatives (what, where, which, etc.) come in sentences, they are used at the beginning of the sentences before helping verbs (is, are, am).
- A question mark (?) is taken at the end of the sentence to show the interrogative sentence.
- The name of the person always starts with a capital letter, as (Aslam, Ali, Akram, Saira, etc.).
- The pronoun (“I”) is written always in capital letter.
Examples of Interrogative Sentences:
There are some examples of interrogative sentences in present continuous tenses:
- Is he going to school?
(Helping Verb: Is, Subject: he, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Is she going to school?
(Helping Verb: is, Subject: she, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Are they going to school?
(Helping Verb: Are, Subject: they, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Are we going to school?
(Helping Verb: Are, Subject: we, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Are you going to school?
(Helping Verb: Are, Subject: You, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Am I going to school?
(Helping Verb: Am, Subject: I, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Is it raining?
(Helping Verb: Is, Subject: it, Main Verb: rain, Add: ing)
- Is Ali eating apples?
(Helping Verb: Is, Subject: Ali, Main Verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: apples)
- Are they flying kites?
(Helping Verb: Are, Subject: They, Main Verb: fly, Add: ing, Object: kites)
- Is Haroon plucking the flowers?
(Helping Verb: Is, Subject: Haroon, Main Verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers)
- Am I singing a song?
(Helping Verb: Am, Subject: I, Main Verb: sing, Add: ing, Object: a song)
- Where are you going to school?
(Interrogative: Where, Helping Verb: are, Subject: you, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- When are they coming to Lahore?
(Interrogative: When, Helping Verb: are, Subject: they, Main Verb: come, Add: ing, Object: to Lahore)
- What are you doing today?
(Interrogative: What, Helping Verb: are, Subject: you, Main Verb: do, Add: ing, Object: today)
These sentences describe actions to ask questions that are currently being performed.
3. Negative Sentences
Negative sentences in the present continuous tense are used to describe actions that are not currently doing. They help to clarify that something is not happening right now or activities that are being denied.
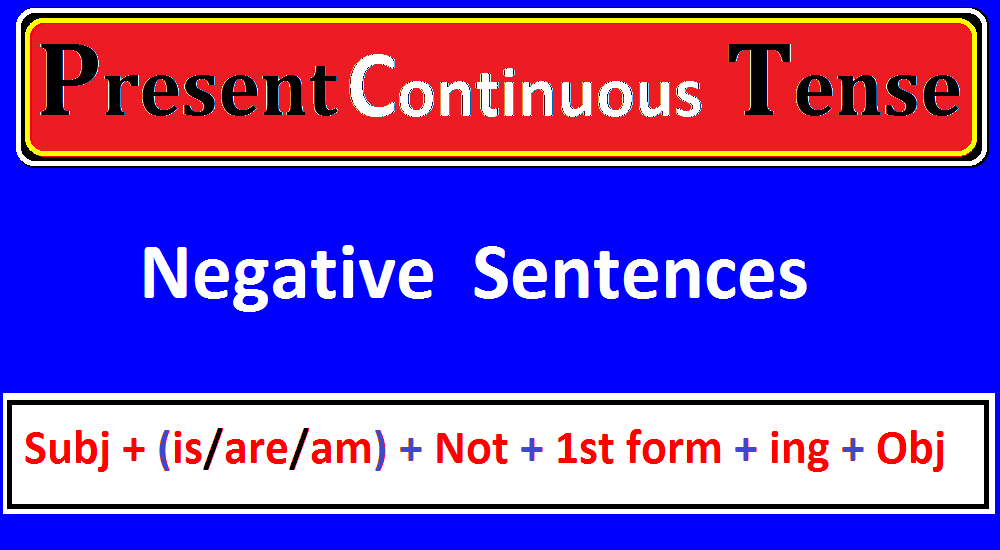
Formation of Negative Sentence in the Present Continuous Tense.
Formula of Negative Sentence:
The formula of a negative sentence in the present continuous tense is the following:
Subject + (Helping Verb) is/are/am + not + 1st form of verb + ing + (Object)
Note Points:
- In negative sentences, the helping verb (is, are, am) comes after the subject.
- The main verb always remains in the first form of the verb with “ing,” like a positive and interrogative sentence in the present continuous.
- “Not,” the word is added after the helping verb (is, are, am) to indicate the negative sentence.
- A full stop (.) is taken at the end of the sentence, like a positive sentence in the present continuous.
Examples of Negative Sentences:
There are some examples of negative sentences in present continuous tenses:
- He is not going to school.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: is, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- She is not going to school.
(Subject: She, Helping Verb: is, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- They are not going to school.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: are, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- We are not going to school.
(Subject: We, Helping Verb: are, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- You are not going to school.
(Subject: You, Helping Verb: are, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- I am not going to school.
(Subject: I, Helping Verb: am, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- It is not raining.
(Subject: It, Helping Verb: is, Negative: not, Main Verb: rain, Add: ing)
- Akram is not eating apples.
(Subject: Akram, Helping Verb: is, Negative: not, Main Verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: apples)
- They are not flying kites.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: are, Negative: not, Main Verb: fly, Add: ing, Object: kites)
- Haroon is not plucking the flowers.
(Subject: Haroon, Helping Verb: is, Negative: not, Main Verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers)
- Rani is not coming to the party.
(Subject: Rani, Helping Verb: is, Negative: not, Main Verb: come, Add: ing, Object: to the party)
These sentences describe actions that are not being taken at the present time.
Conclusion:
The formation of the present continuous tense is essential for clear and accurate communication in English grammar. It helps to convey the right meaning in sentence. Remember the rules of present continuous tense for making the correct sentences.