A complete idea is expressed by a group of words called a sentence. | Components of a Sentence | Types of Sentence in English Grammar with Examples.
Sentence Definition:
A sentence is a set of words that come together to express a complete thought. It typically includes a subject and a predicate, forming a coherent statement, question, exclamation, or command. Sentences can vary in length and complexity, ranging from a single word to elaborate constructions, but their primary function is to convey meaning clearly and effectively in communication.
What Is a Sentence?
A sentence in English is a structured group of words that expresses a complete idea or thought. At its core, it usually consists of a subject, which indicates what the sentence is about, and a predicate, which tells something about the subject.
Sentences serve as the building blocks of communication, allowing us to make statements, ask questions, give commands, or express exclamations. They can be simple, with just a few words, or complex, with multiple clauses and phrases, but their primary goal is to convey clear and meaningful messages.
Components Of Sentence In English
Sentences are the fundamental units of meaning in any language. When you know how subjects, predicates, objects, complements, modifiers, phrases, and clauses fit together, you can create clear and compelling sentences. Understanding the components of a sentence is like understanding the pieces of a puzzle. They can enhance both your writing and speaking skills.
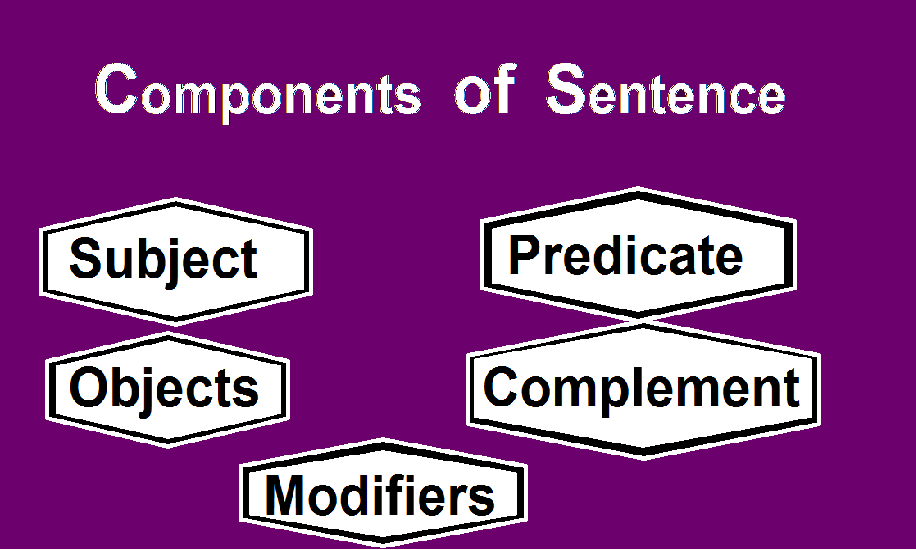
The components of a sentence in English Grammar are:
- Subject
- Predicate
- Objects
- Complement
- Modifiers
1. Subject:
The person, place, thing, or idea that maintains the activity or is being described is the subject of the sentence. It’s what the sentence is about. Identifying the subject is the first step in understanding sentence structure.
– Examples:
- The cat sleeps on the mat.
- She enjoys reading novels.
In these examples, “the cat” and “she” are the subjects performing the actions of sleeping and enjoying.
2. Predicate:
The predicate is what the subject does or is. It includes the verb and anything that modifies the verb or completes its meaning.
– Examples:
- The dog sleeps on the mat.
- He enjoys reading novels.
Here, “sleeps on the mat” and “enjoys reading novels” are the predicates, providing information about what the subjects are doing.
3. Objects:
Objects receive the action of the verb and are often the nouns or pronouns that follow the verb in a sentence.
There are two main types of objects; direct objects and indirect objects.
Direct Object
She reads a book.
“A book” is the direct object that is being read.
Indirect Object
She gave her friend a gift.
Her friend is the indirect object receiving the direct object (a gift).
4. Complement:
A complement completes the meaning of the subject or the verb. Both subject and object complements are noticed.
Subject Complement
He is a teacher.
A teacher describes the subject (he).
Object Complement
They elected her president.
The president describes the direct object (her).
5. Modifiers:
Modifiers add detail and depth to sentences. They can be adjectives, adverbs, phrases, or clauses that provide additional information about the subjects, objects, or verbs.
Adjective (modifying a noun)
The blue car sped past.
“Blue” modifies car.
Adverb (modifying a verb)
She sings beautifully.
“Beautifully” modifies songs.
Types of Sentence in English
English sentences can be divided into groups according to their structure and purpose. Understanding these types can help you communicate more effectively. Each type serves a different role in conveying information, asking for information, giving directions, or expressing emotions.
Types of Sentences According to Structure
Sentence structure refers to the way in which words and phrases are arranged to form grammatically correct sentences in a language. It includes elements such as word order, punctuation, and the relationship between different parts of a sentence in English(subject, verb, object, etc.).
On the basis of structure, there are four main kinds of sentences in English grammar;
- Simple Sentences
- Compound Sentences
- Complex Sentences
- Compound-Complex Sentences
1. Simple Sentences:
A simple sentence is made up of one independent clause that expresses a whole idea and has a subject and a predicate (verb), and it expresses a complete thought.
– Example:
- She goes to the gym.
- He runs every morning.
- She reads every night.
2. Compound Sentences:
A compound sentence consists of two or more independent clauses joined by coordinating conjunctions (such as and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet) or by semicolons.
– Example:
- He likes to run, and he prefers to swim.
- She runs every evening, and she enjoys it.
- She reads every night, and she enjoys it.
3. Complex Sentences:
A complex sentence contains an independent clause and at least one dependent clause introduced by subordinating conjunctions such as “although,” “because,” or “while”.
– Example:
- It was raining, so he grabbed an umbrella.
- Although she runs every morning, she prefers jogging in the evening.
- Although he reads every night, he still finds time to watch TV.
4. Compound-Complex Sentences:
There are always two independent clauses and one dependent clause in a compound-complex statement.
– Example:
- He enjoys playing tennis, but he prefers watching soccer because it reminds him of his childhood.
- He runs every morning, and he feels energised, although he prefers jogging in the evening.
- She reads every night, but she also watches TV because she likes to relax.
These sentence structures can vary in complexity and are essential for constructing clear and meaningful communication in written and spoken English.
Types of Sentences According to Function
On the basis of function, there are four types of sentences in English grammar. They are the vehicles through which we express thoughts, ask questions, give commands, and share information.
- Declarative Sentences
- Interrogative Sentences
- Imperative Sentences
- Exclamatory Sentences
1. Declarative Sentences:
Declarative sentences are the most common type, used to make a statement or provide information. They end with a period.
– Example:
- She is going to the store.
- The sun rises in the east.
2. Interrogative Sentences:
Interrogative sentences ask a question and end with a question mark.
– Example:
- Are you coming with us?
- Where are you going?
3. Imperative Sentences:
Imperative sentences give commands, instructions, or requests; requests; they can make requests. These sentences often start with the verb and end with a period.
– Example:
- Please pass the salt.
- Please close the door.
4. Exclamatory Sentences:
Exclamatory sentences indicate extreme feelings of surprise and end with an exclamation sign.
– Example:
- What a beautiful day!
- What a beautiful sunset!
Conclusion:
Sentences are the building blocks of English communication. Understanding their components, types, and structures is essential for effective writing and speaking. By mastering the art of constructing varied and error-free sentences, you can convey your thoughts clearly and engagingly. So, the next time you write or speak, remember the power of a well-crafted sentence in English to make your message shine.