Formation of The Past Continuous Tense Definition | Past Continuous Tense Structure of Positive, Negative and Interrogative sentences in English Grammar.
Definition of The Past Continuous Tense:
The Past Continuous Tense, also called the past progressive, is used to show that an action was taking place for a period of time in the past.
What is Past Continuous Tense?
The past continuous tense is used to describe actions or events that took place at a certain point in the past. It is usually called the past progressive tense because it shows that something was developing during time.
It is especially useful for describing background actions or events that were happening while something was happening.
Formation Of The Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense is formed with “ing” as the first form of the verb and the helping verb (was, were) in affirmative sentences, interrogative sentences, and negative sentences.
1. Affirmative Sentence Structure of Past Continuous Tense
Past continuous tense affirmative or assertive sentences are used to express actions that were ongoing or happening at a specific time in the past. In an aggressive sentence, we simply state that some work was in progress.

The past continuous tense structure of an affirmative sentence is given.
Affirmative Sentence Formula of Past Continuous Tense:
Past continuous tense formula of an affirmative sentence is the following;
Subject + (Helping Verb) was/were + 1st form of verb + ing + (Object)
Note Points:
- Helping verbs (was, were) are used before the main verb and after the subject.
- “Was” the auxiliary verb is used for singular nouns, subjects, and third person singular pronouns (He, She, It). It is also used for the first person singular pronoun (“I”).
- “Were” the helping verb is used with plural subjects and pronouns (we, you, they).
- “Ing” is added at the end of the base form of the verb, as (“eat” becomes “eating”).
- A full stop (.) is used at the end of a sentence to indicate a past continuous positive sentence.
Affirmative Sentences Examples of Past Continuous Tense:
There are some past continuous tense examples of assertive sentences exercises;
- He was going to school.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: was, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- She was going to school.
(Subject: She, Helping Verb: was, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- They were going to school.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: were, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- We were going to school.
(Subject: We, Helping Verb: were, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- You were going to school.
(Subject: You, Helping Verb: were, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- I was going to school.
(Subject: I, Helping Verb: was, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- It was raining.
(Subject: It, Helping Verb: was, Main Verb: rain, Add: ing)
- Ali was eating food.
(Subject: Ali, Helping Verb: was, Main Verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: food)
- They were flying kites.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: were, Main Verb: fly, Add: ing, Object: kites)
- Nazia was plucking the flowers.
(Subject: Nazia, Helping Verb: was, Main Verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers)
- The girls were smiling.
(Subject: The girls, Helping Verb: were, Main Verb: smile, Add: ing)
These sentences highlight an action that continued in the past without defence or unbroken.
2. Interrogative Sentence Structure of Past Continuous Tense
Past continuous tense interrogative sentences are used to ask about actions that continued at a specific time in the past. These sentences are made by changing the order of the subject and using the helping verb (was/were) as the subject.
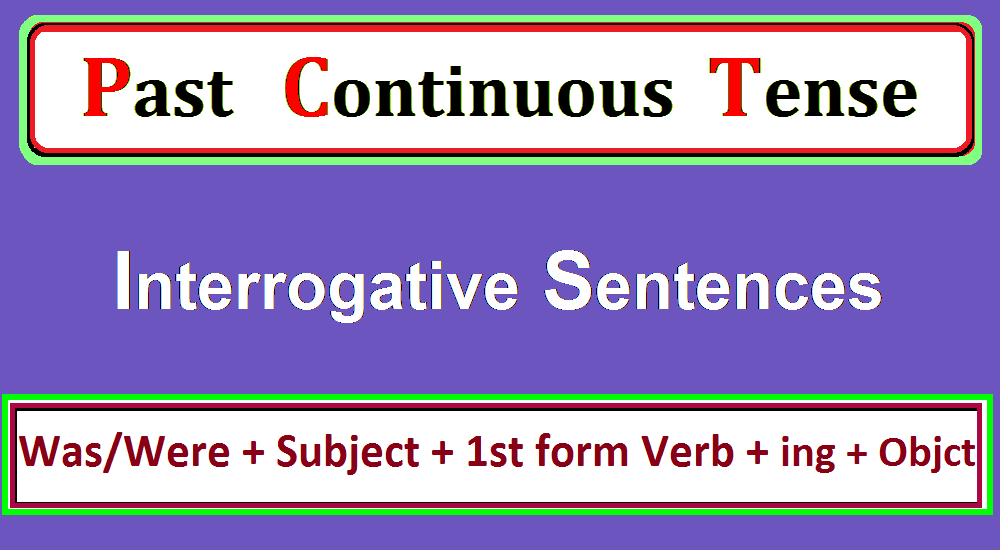
The past continuous tense formation of an interrogative sentence is given.
Interrogative Sentence Formula of Past Continuous Tense:
The formula for the past continuous tense of an interrogative sentence is the following;
Was/Were (Helping Verb) + Subject + 1st form of verb + ing + (Object)
Note Points:
- The helping verb (was/were) comes before the subject to indicate a question sentence.
- The main verb is always the first form of the verb with “ing” like positive sentences in the past continuous.
- A question mark (?) is placed at the end of a sentence to indicate the interrogative sentence in the past continuous.
- If interrogatives (what, where, who, etc.) are in the sentences, they are used at the beginning of the sentences before the helping verb (was/were).
Interrogative Sentences Examples of Past Continuous Tense:
Some examples of interrogative sentences in the past continuous tense are;
- Was he going to school?
(Helping Verb: Was, Subject: he, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Was she going to school?
(Helping Verb: Was, Subject: she, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Were they going to school?
(Helping Verb: Were, Subject: they, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Were we going to school?
(Helping Verb: Were, Subject: we, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Were you going to school?
(Helping Verb: Were, Subject: you, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Was I going to school?
(Helping Verb: Was, Subject: I, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- Was it raining?
( Helping Verb: Was, Subject: it, Main Verb: rain, Add: ing)
- Was Ali eating apples?
(Helping Verb: Was, Subject: Ali, Main Verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: apples)
- Were they flying kites?
(Helping Verb: Were, Subject: they, Main Verb: fly, Add: ing, Object: kites)
- Was Haroon plucking the flowers?
(Helping Verb: Was, Subject: Haroon, Main Verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers)
- Was I singing a song?
(Helping Verb: Was, Subject: I, Main Verb: sing, Add: ing, Object: a song)
- Where were you going?
(Interrogative: Where, Helping Verb: were, Subject: you, Main Verb: go, Add: ing)
- When were they going to Lahore?
(Interrogative: When, Helping Verb: were, Subject: they, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to Lahore)
- What were we doing yesterday?
(Interrogative: What, Helping Verb: were, Subject: we, Main Verb: do, Add: ing, Object: yesterday)
These sentences highlight that questions are used to ask about past actions at particular points in the past.
3. Negative Sentence Structure of Past Continuous Tense
Past continuous tense negative sentences are used to describe actions that were not happening at a specific time in the past. To make a negative sentence, we simply add “not” after the helping verb (was/were).
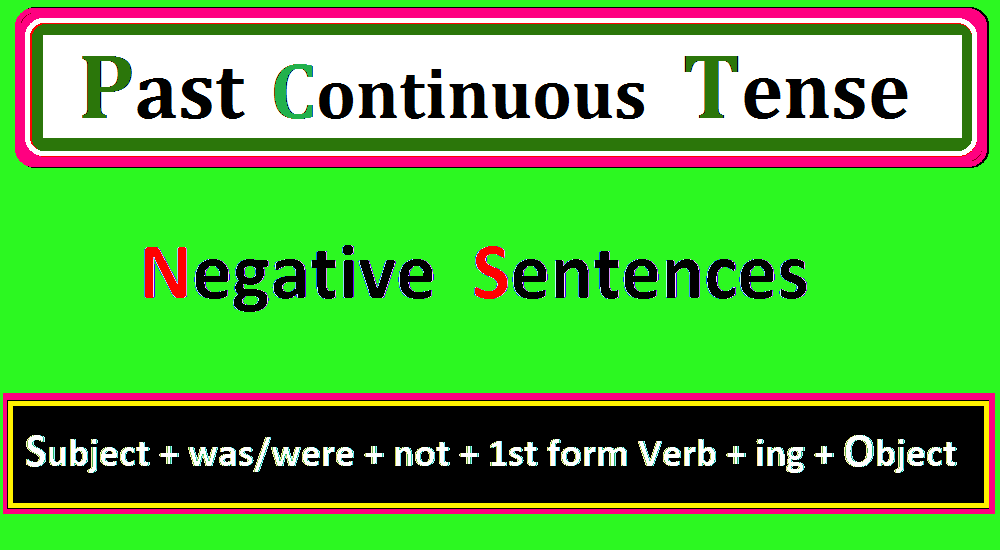
The past Indefinite tense formation of a negative sentence is given.
Negative Sentence Formula of Past Continuous Tense:
The past continuous tense formula for a negative sentence is the following;
Subject + (Helping Verb) was/were + not + 1st form of verb + ing + (Object)
Note Points:
- In negative sentences, the helping verb (was/were) comes after the subject.
- The main verb remains always with “ing” in the first form of the verb, as positive and interrogative sentences in the past continuous.
- The word “not” is added after the helping verb (was/were) to indicate a negative sentence.
- A full stop (.) is placed at the end of a sentence such as a positive sentence in the past continuous.
Negative Sentences Examples of Past Continuous Tense:
Here are some examples of negative sentences in the past continuous tense;
- He was not going to school.
(Subject: He, Helping Verb: was, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- She was not going to school.
(Subject: She, Helping Verb: was, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- They were not going to school.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: were, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- We were not going to school.
(Subject: We, Helping Verb: were, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- You were not going to school.
(Subject: You, Helping Verb: were, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- I was not going to school.
(Subject: I, Helping Verb: was, Negative: not, Main Verb: go, Add: ing, Object: to school)
- It was not raining.
(Subject: It, Helping Verb: was, Negative: not, Main Verb: rain, Add: ing)
- Akram was not eating mangoes.
(Subject: Akram, Helping Verb: was, Negative: not, Main Verb: eat, Add: ing, Object: mangoes)
- They were not flying kites.
(Subject: They, Helping Verb: were, Negative: not, Main Verb: fly, Add: ing, Object: kites)
- Najma was not plucking the flowers.
(Subject: Najma, Helping Verb: was, Negative: not, Main Verb: pluck, Add: ing, Object: the flowers)
- Rani was not coming to the party.
(Subject: Rani, Helping Verb: was, Negative: not, Main Verb: come, Add: ing, Object: to the party)
These sentences highlight that an action was not in progress at a particular time in the past.
Conclusion:
Understanding the past continuous tense formation will enable you to speak clearly and create assertive or aggressive sentences, interrogative sentences, and negative sentences in English grammar. In this article, all the past continuous structures are given to easily express past actions.